Will my hair be as thick as before?
While most people pay attention to the words “hair transplant,” a particular photo pops into their mind: faux, “pluggy” looking hair that’s glaringly the result of a cosmetic system instead of a natural hairline.
Sadly, hair transplants have terrible popularity because of the old Eighties “hair plug” procedures, which transplanted hairs in plugs of numerous follicles and created an unusual, unnatural-looking hairline.
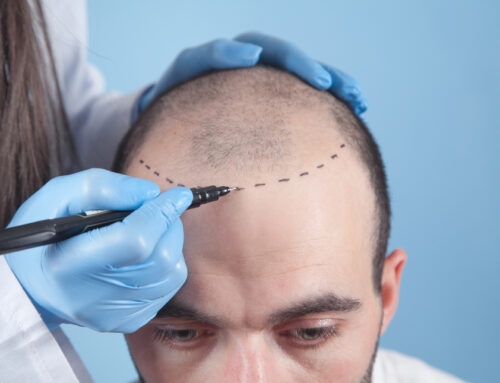
The fact is that nowadays hair transplant technology permits you to add thickness to your hair and fill in a receding hairline without the fake, plug-like appearance of older treatments.
However, hair transplants aren’t miracles, and there are nonetheless potential downsides that you must be aware of.
In this manual, we’ll explain how cutting-edge hair transplants work and how they can be used to fill on your hairline and reverse the male sample baldness results. We’ll also cover the downsides of hair transplants and explain how many of the procedure’s limitations should affect you.
In case you’re considering getting a hair transplant, the data below can help you make a more knowledgeable, confident choice approximately whether the process is the suitable alternative for you.
What’s a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a cosmetic process that includes harvesting hairs from an inevitable part of your scalp (known as the “donor web page”) and transplanting them onto a whole piece of your scalp.
In short, getting a hair transplant takes hair from areas of your scalp that aren’t stricken by male sample baldness and shifts it to places that might be thinning or bald.
Hair transplants work because no longer all of the hair on your head is laid low with DHT, the primary hormone that reasons baldness. With the aid of transferring DHT-resistant strands from the lower back and sides of your head to the front, a hair transplant health practitioner can be able to provide you with a thick hair.
In the beginning, hairline transplants concerned putting off and transplanting hairs using “plugs,” which were agencies of numerous hair follicles in clusters.
while hair plugs worked as a way to fill in a receding hairline, they usually appeared unnatural due to the truth that hair grafts have been grouped into separate regions, once in a while with a significant hole in among each “plug.”
Nowadays, hair transplants are tons more sophisticated.
From a cultured perspective, a hair transplant done by using an experienced surgeon will look and experience much like a natural hairline, assuming you’ve got enough donor hair to be had and the capability to grow hair on the regions of your scalp that want it.
FUE vs. FUT: What’s The difference?
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) are popular surgical hair recuperation strategies.
Each approach produces a similar result, albeit with a few variations. FUE includes the process of extracting small “segments” of one to four hairs from the head using a surgical tool. Those hairs are then transplanted onto the top of the top to restore a hairline or offer extra thickness.
The advantage of FUE is that it doesn’t produce a huge scar. Instead, it creates masses of tiny spots that are much less visible after healing, especially for people with light hair who won’t be able to absolutely cowl a conventional “strip” hair transplant scar.
FUT, then again, includes casting off a strip of pores and skin from the scalp. Hairs are extracted from this strip in groups of 1 to 4. After removing the hair follicles, the healthcare professional can transplant the strands onto the scalp’s pinnacle to fill in the hairline or crown.



Leave A Comment